Samples a 3-dimensional grid of values of a function f.
gx, gy, and gz give the origin, number of steps and step width of the grid for the x, y and z direction, e.g. gx = (x0, nx, dx), gy = (y0, ny, dy) and gz = (z0, nz, dz).
So
![]() values of the function f are sampled
at locations
values of the function f are sampled
at locations ![]() with
with
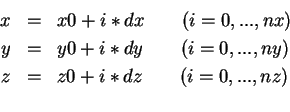
In the C++ class hierarchy the class which is created by the GRIDEVAL3 keyword is derived from a general 3-dimensional grid class (see GRID3, 6.6.3), so that it can be used at any places where a 3-dimensional grid is expected (with the same number format of course).
The following variations of this keyword exist (some of them define the same internal structures, and are only defined to allow consistent naming conventions):
| Keyword | numbers |
| GRIDEVAL3 | float |
| GRIDEVAL3_F | float |
| GRIDEVAL3_D | double |